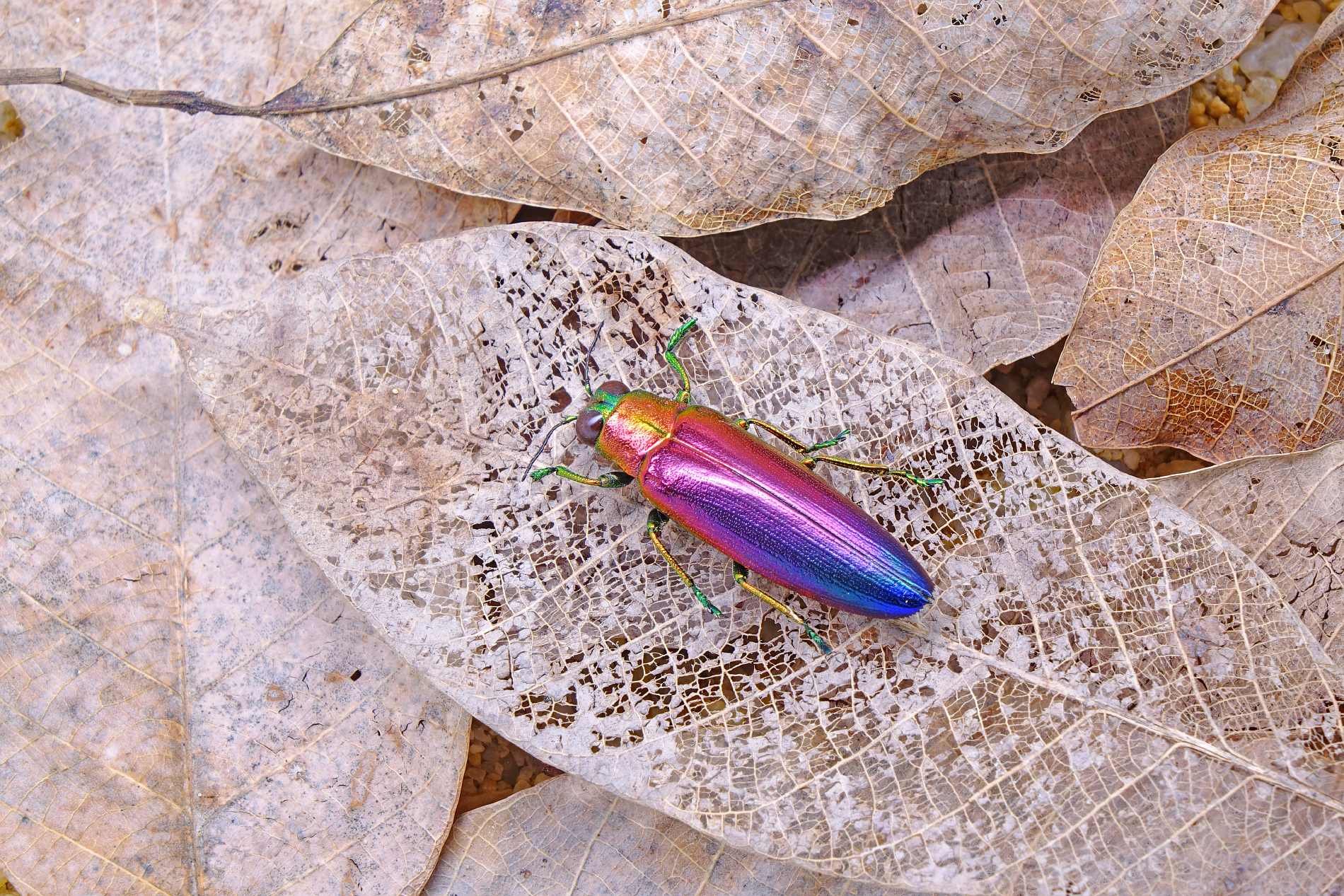
Darkling Beetles (Tenebrionids) Missouri Department of Conservation
4.6 (769) · € 22.50 · Auf Lager
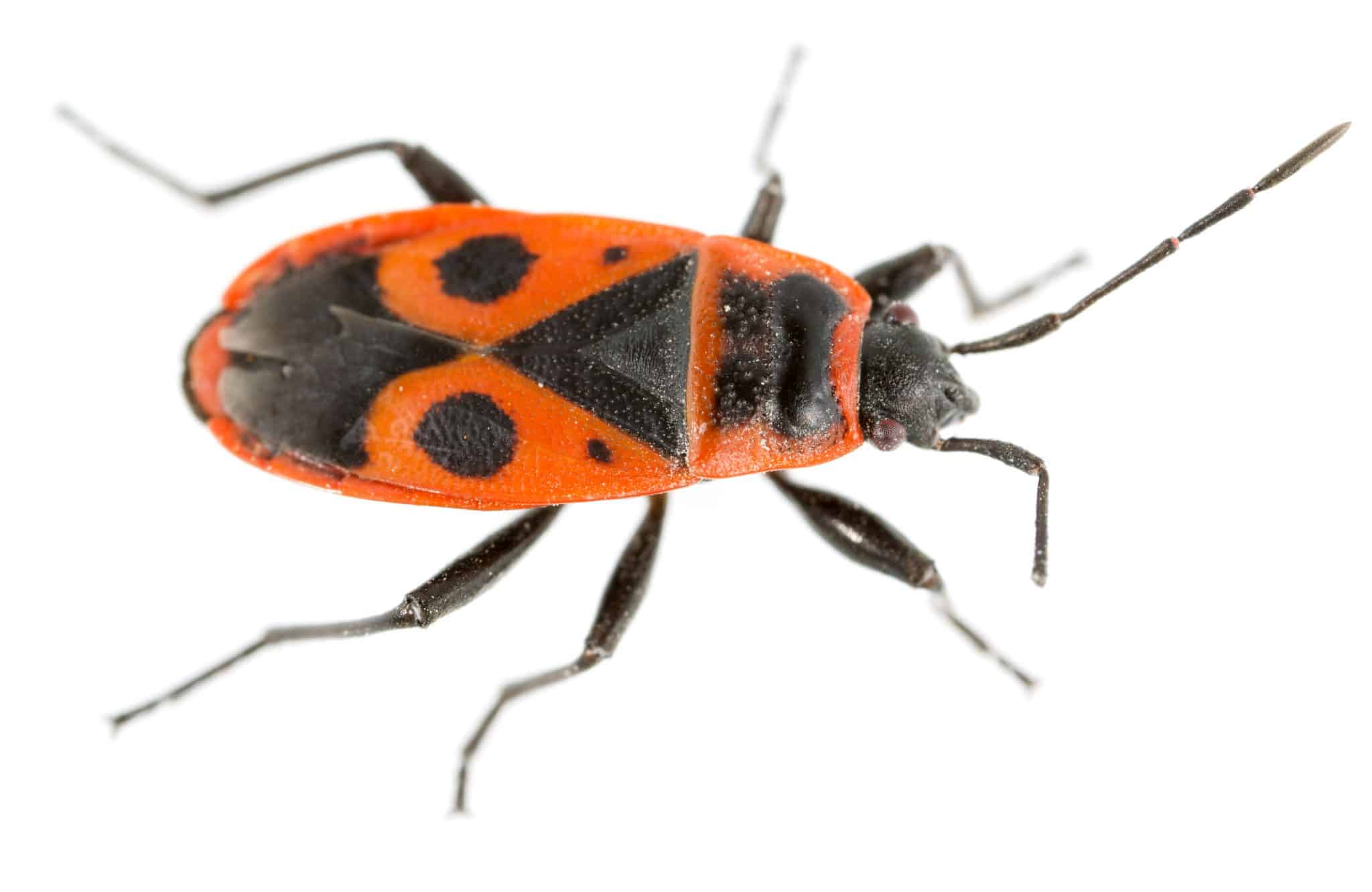
Darkling beetles are a very large family of beetles. Most are dull black or brown, crawl on the ground, and are scavengers. Many of them — lacking remarkable colors, pincers, horns, or odd-shaped antennae — resemble what you might call a “base-model” beetle, or a beetle’s beetle. Since they’re sort of “normal-looking” beetles, how do you tell if a beetle is a darkling beetle? There are a suite of characters that, taken together, help ID beetles in this group: Color: typically black or brown, often dull, sometimes shiny; sometimes with other patterns or colors (notably red). Some have fine hairs or a fuzzy or waxy coating. Size and shape: Varies widely. Most are oval or elongated. Globally they range from extremely tiny to 3 inches; in our region, the largest are only to about 1½ inches. Texture: the cuticle (exterior) is hard and thick. The surface is sometimes smooth, sometimes lumpy or knobby, sometimes ridged or pitted. Head: fairly wide, rounded in front; the jaws are not easy to see from above (unlike the easy-to-see pincerlike jaws of ground beetles, tiger beetles, and stag beetles). Antennae: usually with 11 segments; appear beadlike or threadlike; often slightly clubbed (with the outer segments gradually wider). One subgroup has the outermost antennal segment elongated. The antennae emerge from beneath a shelflike structure in front of the eyes. Eyes: the shelflike structure in front of each eye intrudes into the eye, making the eye appear notched (not perfectly rounded or oval). Feet (tarsi): the front 2 pairs of legs have tarsi with 5 segments; the back pair of legs have tarsi with 4 segments. Locomotion: Usually by walking. Some species can fly and may be attracted by lights at night. Many species are flightless; some have the elytra (shell-like forewings) fused together, with no visible split down the back. The ones with fused forewings are especially common in desert habitats. Larvae are hard-bodied, cylindrical, with 6 short legs behind the head; they drag the long hind portion of the body along. If you are familiar with mealworms, picture them: mealworms are the larvae of certain types of darkling beetles. The larvae of some types of darkling beetles are called false wireworms, because they can resemble the larvae of click beetles (called wireworms).

Darkling beetle - Wikipedia

Darkling Beetle Problems: Prevention and Management - Epic Gardening

Do Darkling Beetles Bite? Debunking Myths and Facts - What's That Bug?

Do Darkling Beetles Bite? Debunking Myths and Facts - What's That Bug?

Darkling Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures

Darkling Beetle Life Cycle: A Fascinating Journey Explained - What's That Bug?
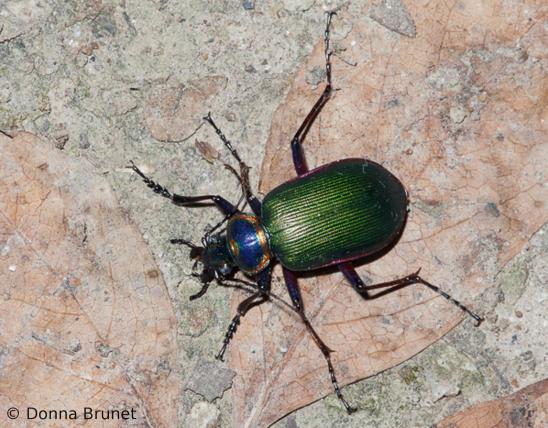

Darkling Beetles (Tenebrionids) Missouri Department of Conservation
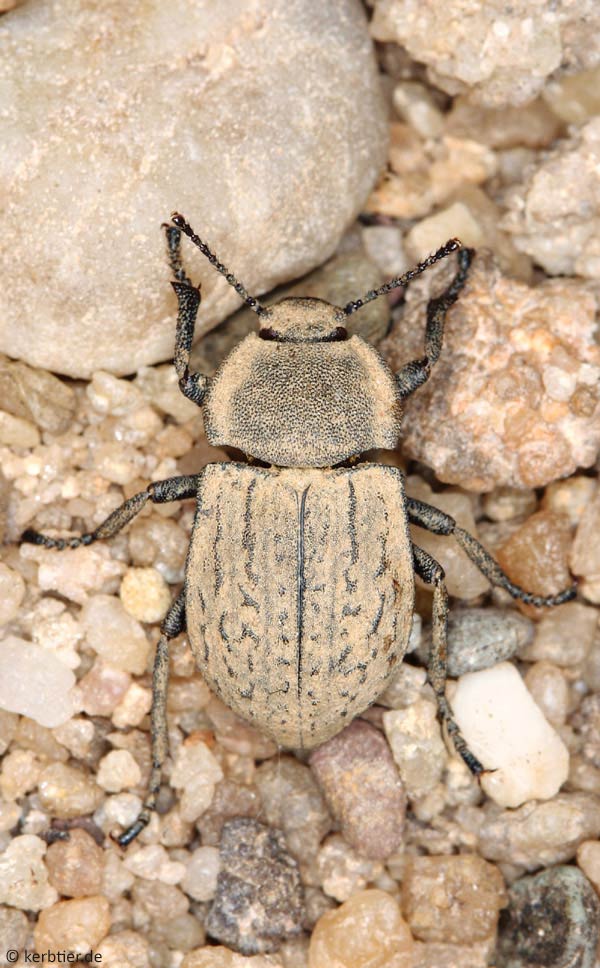

Photo overview Tenebrionidae (darkling beetles) of Germany
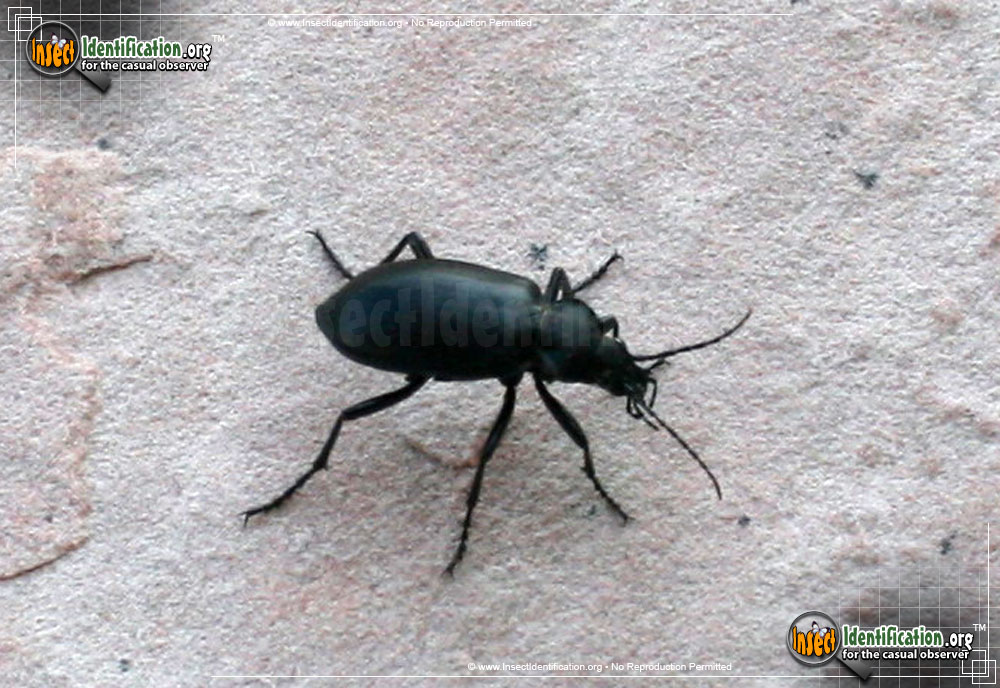

Darkling Beetle

Armoured tank beetle”

Additions to the knowledge of the diversity of darkling beetles (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) from Turkey with new records and taxonomic notes

Illustrated Catalog of the Subtribe Helopinina Lacordaire (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae: Blaptinae: Pedinini)

Fungus Weevils Missouri Department of Conservation

Darkling Beetle Life Cycle: A Fascinating Journey Explained - What's That Bug?

Type Catalogue of Darkling Beetles (Tenebrionidae) Preserved in the Hungarian Natural History Museum / A Magyar Természettudományi Múzeum Gyászbogártípusainak (Tenebrionidae) Katalógusa